THE 4CS – 4 QUALITY CRITERIA OF DIAMONDS
CUT, CLARITY, COLOR & CARAT
Every diamond has its own distinguishing characteristics. The 4Cs—cut, clarity, color and carat weight—are the globally accepted standards for assessing the quality of a diamond.
The Most Precious Stones.
Our talented artisans cut diamonds to the highest standards.
Only the most expertly crafted diamonds earn the right to be placed on your custom jewelry.
Every diamond has its own distinguishing characteristics. The 4Cs—cut, clarity, color and carat weight—are the globally accepted standards for assessing the quality of a diamond.
Cut determines the beauty and
shine of the stone.
More than any other factor, Cut determines the beauty and shine of the stone. It is determined by proportion, system and polish. E.E.E diamonds, from the smallest to the largest stone are cut to exacting standards.
Cutting is the processing technique for polishing and cutting diamonds in the rough state. Ores that transmit light like diamonds have the property of having a high refractive index. Light enters at various angles and is refracted internally. At this time, if the incident angle exceeds a certain range, an effect called “total reflection” occurs. Total reflection is a phenomenon in which light is trapped and does not come out. Since the inside of the diamond is very likely to undergo total internal reflection, the light is not dispersed and therefore has a strong sparkle.
Brilliant Cut (Round/ Oval/ Pear Shape/ Marquise/ Heart Shape)
Step Cut (Emerald Cut of Diamond)
Princess Cut
Rose Cut
Half Moon Cut
Trilliant Cut
Long Octagon Cut
Star Cut
Lily Cut
Asher Cut

The Proportion is an important factor in the shine of the diamond.
It only shows the shape of the diamond numerically and does not evaluate any details.
The Symmetry is evaluated by taking into account factors such as girdle ellipticity, table ellipticity, eccentricity, tilt, uneven girdle thickness and eccentricity of the curette. If the proportion is good, but the symmetry is bad the condition of the angle of incidence and reflection of light will be broken. Symmetry is also a factor that greatly affects the diamond’s brightness.
The Polish is a good indicator of how well diamonds are finished. The quality of polishing is the surface roughness of the entrance and reflection surfaces. Poor surface roughness can cause diffused reflection of light. The effect of diffuse reflection is that although the absolute value of the light amount is slightly reduced, it can also cause a whitish glow.
Clarity measures the purity and
rarity of the stone.
Clarity is the presence or absence of impurities and scratches. Impurities in diamonds not only affect light transmittance, but also cause diffuse reflection blurring the rainbow-colored light characteristic of diamond and giving it a whitish glow.
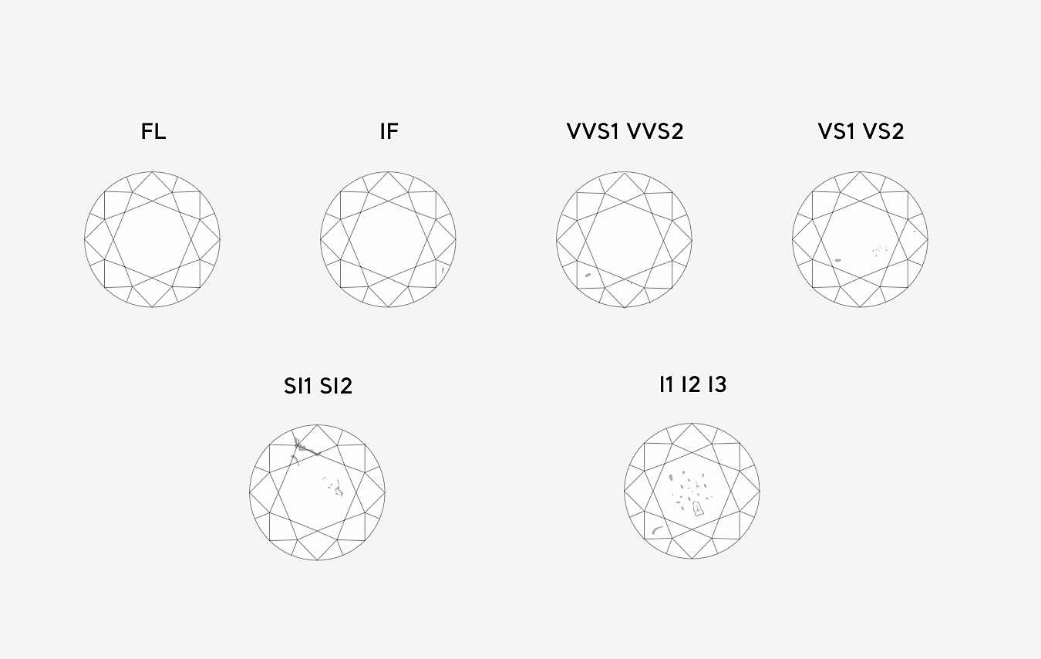
Clarity grades are FL, IF, VVS1, VVS2, VS1, VS2, SI1, SI2, I1, I2, and I3, starting from the best. According to Clarity’s appraisal, “I” grades have inclusions that are visible to the naked eye. Use a 10x magnifier to determine the size of the wound, its size, volume and location. This clarity grade is the same as the color and is universal.
Even the most skilled person cannot find inclusions and wounds.
No inclusions found, slight scratches on surface.
Really small inclusions and scratches can be found.
Slight inclusions and scratches can be found.
There are slight inclusions and scratches that can be found with the naked eye.
Color refers to the natural tint inherent in white diamonds.
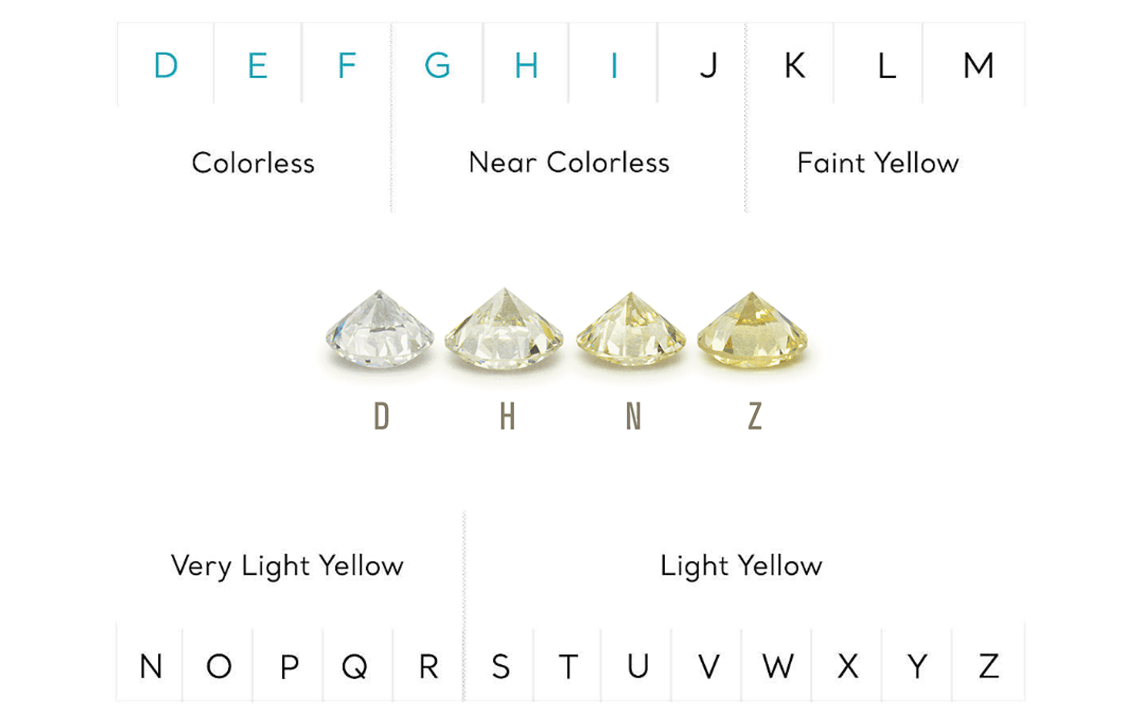
Color refers to the natural tint inherent in white diamonds. In nature, most white diamonds have a slight tint of yellow. The closer to being “colorless” a diamond is, the rarer it is.
As the color gradually changes from transparent to yellow, the color grade goes down from D to Z. The evaluation method and the notation of the color grade are common in all countries and are compared with a color sample called a master stone.
Colorless
Near Colorless
Faint Yellow
Very Light Yellow
Light Yellow
Carat denotes the weight of a diamond
One carat represents .20 grams.
Because carats represent weight and not size, doubling the carat count does not mean that the diamond diameter is doubled. The effect on diameter is the cube root. When the carat is doubled, the diameter is 1.26 times. There is only a 1% difference in diameter between 0.30 carat and 0.31 carat. That said, diamonds of exactly the same carat number will vary in diameter in the form of cuts.
It is important to note that carat weight
does not necessarily denote size.

Learn More about Our Craftmanship